本文作为MySQL使用指南的延申讨论
- 递归
- 行列转换
- 日期/时间处理相关函数
一. 递归
As mentioned previously, recursive common table expressions (CTEs) are frequently used for series generation and traversing hierarchical or tree-structured data.
递归成员不得包含以下结构:
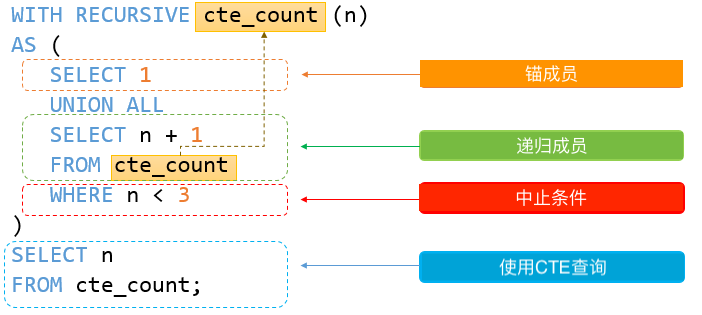
递归公用表表达式 ( CTE) 是一个CTE 它有一个子查询 它引用CTE名称本身. 以下说明了递归CTE的语法
WITH RECURSIVE cte_name AS ( initial_query -- anchor member UNION ALL recursive_query -- 引用CTE名称的递归成员 SELECT * FROM cte_name;递归CTE由三个主要部分组成:
- 初始查询 形成CTE结构的基本结果集. 初始查询部分称为锚成员.
- 递归查询部分是引用CTE名称的查询 因此 它被称为递归成员. 递归成员由
UNION ALL或UNION DISTINCT运算符与锚成员连接.- 终止条件 确保递归成员不返回任何行时停止递归.
递归CTE的执行顺序如下:
- 首先 将成员分为两部分: 锚点和递归成员.
- 接下来 执行锚成员以形成基本结果集(
R0) 并将此基本结果集用于下一次迭代.- 然后 执行带有
Ri结果集作为输入的递归成员并将其Ri+1作为输出.- 之后 重复第三步 直到递归成员返回空结果集 换句话说 满足终止条件.
- 最后 使用
UNION ALL运算符将结果集从R0到Rn组合.
# 生成斐波那契数列
WITH RECURSIVE fibonacci (n, fib_n, next_fib_n) AS
(
SELECT 1, 0, 1
UNION ALL
SELECT n + 1, next_fib_n, fib_n + next_fib_n
FROM fibonacci WHERE n < 10
)
SELECT * FROM fibonacci;
+------+-------+------------+
| n | fib_n | next_fib_n |
+------+-------+------------+
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 |
| 4 | 2 | 3 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 |
| 6 | 5 | 8 |
| 7 | 8 | 13 |
| 8 | 13 | 21 |
| 9 | 21 | 34 |
| 10 | 34 | 55 |
+------+-------+------------+
10 rows in set (0.00 sec)
二. 日历
+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
| 星期一 | 星期二 | 星期三 | 星期四 | 星期五 | 星期六 | 星期日 |
+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
| NULL | NULL | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | NULL | NULL |
+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MySQL root@localhost:(none)> select current_date();
+----------------+
| current_date() |
+----------------+
| 2023-03-13 |
+----------------+
1 row in set
Time: 0.004s
WITH RECURSIVE calendar ( init_date ) AS (
# 生成第一天的数据, 可以使用其他方式来生成
SELECT
subdate( adddate( CURRENT_DATE, INTERVAL 1 DAY ), INTERVAL dayofmonth( CURRENT_DATE ) DAY ) UNION ALL
SELECT
adddate( init_date, INTERVAL 1 DAY )
FROM
calendar
WHERE
# 循环到最后一天
init_date < last_day( CURRENT_DATE )
) SELECT
*
FROM
calendar;
+------------+
| int_date |
+------------+
| 2023-03-01 |
| 2023-03-02 |
| 2023-03-03 |
| 2023-03-04 |
| 2023-03-05 |
| 2023-03-06 |
| 2023-03-07 |
| 2023-03-08 |
| 2023-03-09 |
| 2023-03-10 |
| 2023-03-11 |
| 2023-03-12 |
| 2023-03-13 |
| 2023-03-14 |
| 2023-03-15 |
| 2023-03-16 |
| 2023-03-17 |
| 2023-03-18 |
| 2023-03-19 |
| 2023-03-20 |
| 2023-03-21 |
| 2023-03-22 |
| 2023-03-23 |
| 2023-03-24 |
| 2023-03-25 |
| 2023-03-26 |
| 2023-03-27 |
| 2023-03-28 |
| 2023-03-29 |
| 2023-03-30 |
| 2023-03-31 |
+------------+
31 rows in set (0.00 sec)
WITH RECURSIVE calendar ( init_date ) AS (
SELECT
subdate( adddate( CURRENT_DATE, INTERVAL 1 DAY ), INTERVAL dayofmonth( CURRENT_DATE ) DAY ) UNION ALL
SELECT
adddate( init_date, INTERVAL 1 DAY )
FROM
calendar
WHERE
init_date < last_day( CURRENT_DATE )
) SELECT
init_date,
# 返回日期对应的周
WEEK ( init_date, 1 ) AS wk,
dayofmonth( init_date ) AS dm,
dayofweek( init_date ) AS dw
FROM
calendar;
+------------+------+------+------+
| init_date | wk | dm | dw |
+------------+------+------+------+
| 2023-03-01 | 9 | 1 | 4 |
| 2023-03-02 | 9 | 2 | 5 |
| 2023-03-03 | 9 | 3 | 6 |
| 2023-03-04 | 9 | 4 | 7 |
| 2023-03-05 | 9 | 5 | 1 |
| 2023-03-06 | 10 | 6 | 2 |
| 2023-03-07 | 10 | 7 | 3 |
| 2023-03-08 | 10 | 8 | 4 |
| 2023-03-09 | 10 | 9 | 5 |
| 2023-03-10 | 10 | 10 | 6 |
| 2023-03-11 | 10 | 11 | 7 |
| 2023-03-12 | 10 | 12 | 1 |
| 2023-03-13 | 11 | 13 | 2 |
| 2023-03-14 | 11 | 14 | 3 |
| 2023-03-15 | 11 | 15 | 4 |
| 2023-03-16 | 11 | 16 | 5 |
| 2023-03-17 | 11 | 17 | 6 |
| 2023-03-18 | 11 | 18 | 7 |
| 2023-03-19 | 11 | 19 | 1 |
| 2023-03-20 | 12 | 20 | 2 |
| 2023-03-21 | 12 | 21 | 3 |
| 2023-03-22 | 12 | 22 | 4 |
| 2023-03-23 | 12 | 23 | 5 |
| 2023-03-24 | 12 | 24 | 6 |
| 2023-03-25 | 12 | 25 | 7 |
| 2023-03-26 | 12 | 26 | 1 |
| 2023-03-27 | 13 | 27 | 2 |
| 2023-03-28 | 13 | 28 | 3 |
| 2023-03-29 | 13 | 29 | 4 |
| 2023-03-30 | 13 | 30 | 5 |
| 2023-03-31 | 13 | 31 | 6 |
+------------+------+------+------+
31 rows in set (0.00 sec)
这里涉及到行列转换问题
2.1 行列转换
这里使用MySQL和PostgreSQL进行对比
create table test_b(name char(4), s_type varchar(10), s_value int);
insert into test_b values('alex','weight', 60);
insert into test_b values('alex','age', 60);
insert into test_b values('alex','heigh', 160);
insert into test_b values('tony','weight', 78);
insert into test_b values('tony','age', 35);
insert into test_b values('tony','heigh', 170);
name | s_type | s_value
------+--------+---------
alex | weight | 60
alex | age | 60
alex | heigh | 160
tony | weight | 78
tony | age | 35
tony | heigh | 170
(6 rows)
2.1.1 PostgreSQL
postgresql支持extension
test_db=# select name from pg_available_extensions;
name
---------------------
adminpack
amcheck
autoinc
bloom
bool_plperl
bool_plperlu
btree_gin
btree_gist
citext
cube
dblink
dict_int
dict_xsyn
dummy_index_am
earthdistance
file_fdw
fuzzystrmatch
hstore
hstore_plperl
hstore_plperlu
hstore_plpython3u
insert_username
intagg
intarray
isn
jsonb_plperl
jsonb_plperlu
jsonb_plpython3u
lo
ltree
ltree_plpython3u
moddatetime
old_snapshot
pageinspect
pgcrypto
pgrowlocks
pgstattuple
pg_buffercache
pg_freespacemap
pg_prewarm
pg_stat_statements
pg_surgery
pg_trgm
pg_visibility
pg_walinspect
pldbgapi
plperl
plperlu
plpgsql
plpython3u
plsample
pltcl
pltclu
postgres_fdw
refint
seg
spgist_name_ops
sslinfo
system_stats
tablefunc
tcn
test_bloomfilter
test_ext1
test_ext2
test_ext3
test_ext4
test_ext5
test_ext6
test_ext7
test_ext8
test_ext_cine
test_ext_cor
test_ext_cyclic1
test_ext_cyclic2
test_ext_evttrig
test_ginpostinglist
test_integerset
test_pg_dump
test_predtest
test_rbtree
test_regex
tsm_system_rows
tsm_system_time
unaccent
uuid-ossp
xml2
(86 rows)
CREATE EXTENSIONloads a new extension into the current database. There must not be an extension of the same name already loaded.Loading an extension essentially amounts to running the extension's script file. The script will typically create new SQL objects such as functions, data types, operators and index support methods.
CREATE EXTENSIONadditionally records the identities of all the created objects, so that they can be dropped again ifDROP EXTENSIONis issued.The user who runs
CREATE EXTENSIONbecomes the owner of the extension for purposes of later privilege checks, and normally also becomes the owner of any objects created by the extension's script.Loading an extension ordinarily requires the same privileges that would be required to create its component objects. For many extensions this means superuser privileges are needed. However, if the extension is marked trusted in its control file, then it can be installed by any user who has
CREATEprivilege on the current database. In this case the extension object itself will be owned by the calling user, but the contained objects will be owned by the bootstrap superuser (unless the extension's script explicitly assigns them to the calling user). This configuration gives the calling user the right to drop the extension, but not to modify individual objects within it.
SELECT
*
FROM
crosstab ( 'select name, s_type, s_value from test_b' ) AS ct ( NAME CHAR ( 4 ), weight INT, age INT, heigh INT );
ERROR: function crosstab(unknown) does not exist
# 需要先执行
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS tablefunc;
test_db=# SELECT * FROM crosstab('select name, s_type, s_value from test_b') AS ct(name char(4), weight int, age int, heigh int);
name | weight | age | heigh
------+--------+-----+-------
alex | 60 | 60 | 160
tony | 78 | 35 | 170
(2 rows)
非常简单, 在 postgresql之下.
PostgreSQL: Documentation: 15: F.43. tablefunc
2.1.2 MySQL
MySQL root@localhost:test_db> select name,
-> sum(case when s_type='age' then s_value else 0 end) as age,
-> sum(case when s_type='heigh' then s_value else 0 end) as heigh,
-> sum(case when s_type='weight' then s_value else 0 end) as weight
-> from test_b group by name;
+------+-----+-------+--------+
| name | age | heigh | weight |
+------+-----+-------+--------+
| alex | 60 | 160 | 60 |
| tony | 35 | 170 | 78 |
+------+-----+-------+--------+
2 rows in set
MySQL root@localhost:test_db> select name,
-> max(case when s_type='age' then s_value else 0 end) as age,
-> max(case when s_type='heigh' then s_value else 0 end) as heigh,
-> max(case when s_type='weight' then s_value else 0 end) as weight
-> from test_b group by name;
+------+-----+-------+--------+
| name | age | heigh | weight |
+------+-----+-------+--------+
| alex | 60 | 160 | 60 |
| tony | 35 | 170 | 78 |
+------+-----+-------+--------+
2 rows in set
Time: 0.007s
WITH RECURSIVE calendar ( init_date ) AS (
SELECT
subdate( adddate( CURRENT_DATE, INTERVAL 1 DAY ), INTERVAL dayofmonth( CURRENT_DATE ) DAY ) UNION ALL
SELECT
adddate( init_date, INTERVAL 1 DAY )
FROM
calendar
WHERE
init_date < last_day( CURRENT_DATE )
),
a AS (
SELECT
init_date,
WEEK ( init_date, 1 ) AS wk,
dayofmonth( init_date ) AS dm,
dayofweek( init_date ) - 1 AS dw
FROM
calendar
) SELECT
max(
IF
( dw = 1, dm, NULL )) AS "星期一",
max(
IF
( dw = 2, dm, NULL )) AS "星期二",
max(
IF
( dw = 3, dm, NULL )) AS "星期三",
max(
IF
( dw = 4, dm, NULL )) AS "星期四",
max(
IF
( dw = 5, dm, NULL )) AS "星期五",
max(
IF
( dw = 6, dm, NULL )) AS "星期六",
max(
IF
( dw = 0, dm, NULL )) AS "星期日"
FROM
a
GROUP BY
wk;
+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
| 星期一 | 星期二 | 星期三 | 星期四 | 星期五 | 星期六 | 星期日 |
+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
| NULL | NULL | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | NULL | NULL |
+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
不管是max, min, sum操作, 其原理都是类似的, 但是需要注意不能使用any_value.
2.2 涉及的日期处理函数
- current_date, 当前日期
- subdate, 减掉间隔
- adddate, 增加间隔
- last_day, 返回月的最后一天
- week, 日期所在的周(一年)
- dayofmonth, 日所在的月
- dayofweek, 日所在星期
