一. 前言
1.1 使用环境
os: win10, 64bit pro
database version: 6.x
compass version: 1.34.2
shell version: 1.6.0
mongodump version: 100.6.1
mongorestore version: 100.6.1
Terminal: Fluent Terminal(Powershell, 5.1.19041.2364)
1.2 安装简介
mongodb的主程序安装包除了server之外, 其他组件均不集成在一起, 需要单独下载, 包括shell在内.
mongodb assistance tools download url
解压后, 添加到环境变量即可.
1.3 图形管理工具
-
compass, 这是mongodb官方版本的GUI管理工具, 免费.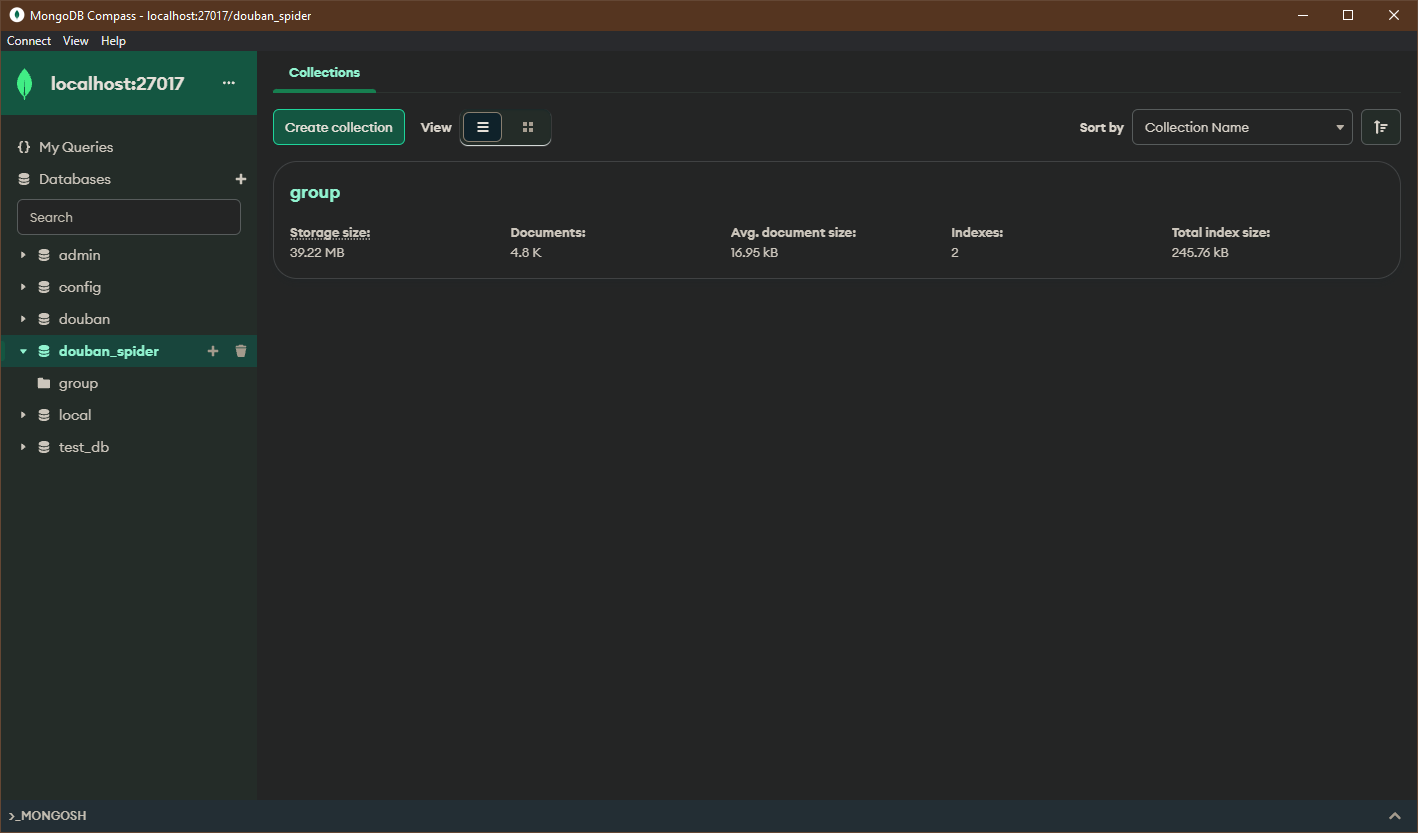
-
navicat premium, 一款极其强大的综合性数据库管理工具, 付费.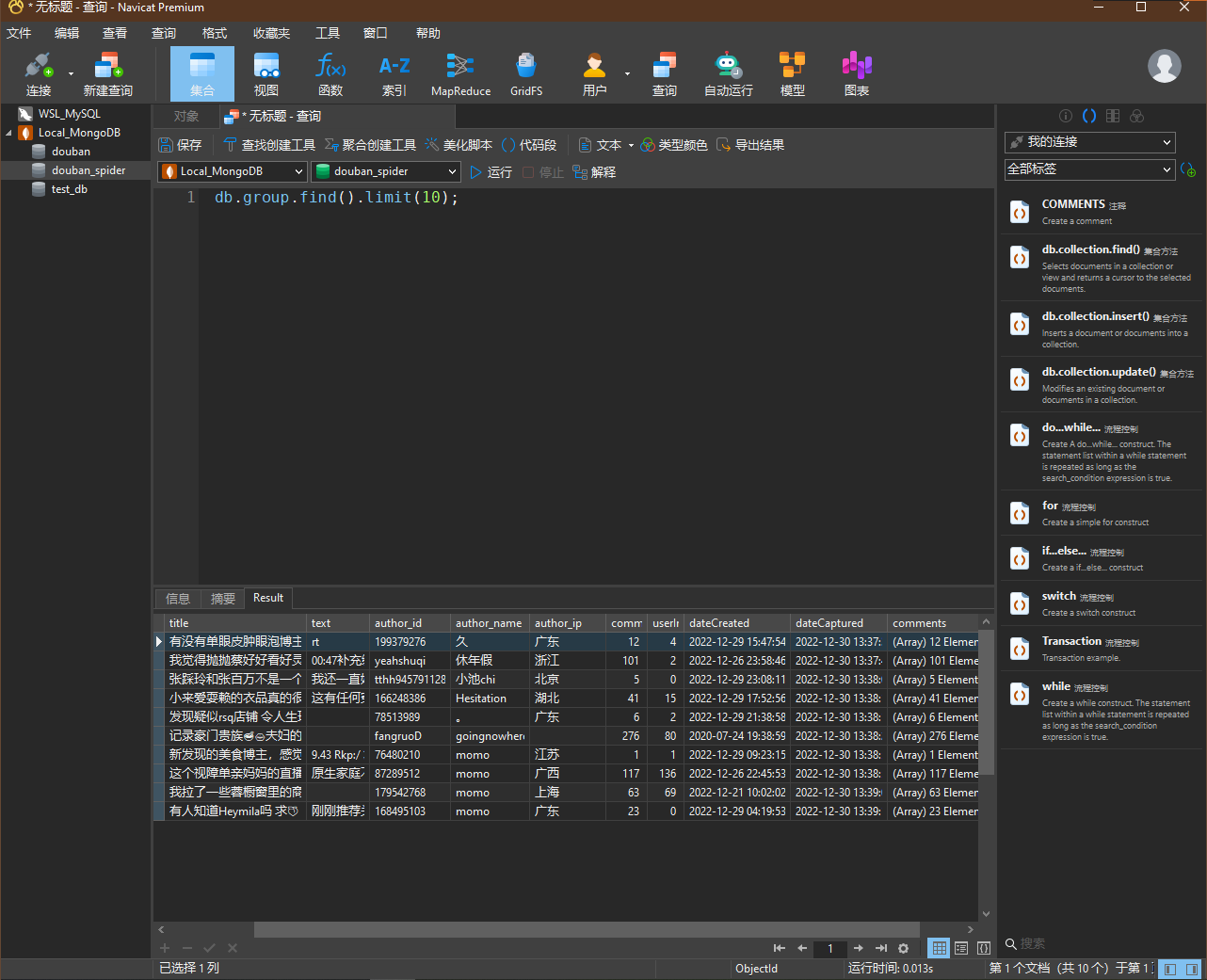
相比于
compass, navicat对于嵌套文档的显示效果更为直观.
二. 基本概要
3.1 BSON
BSON是一种计算机数据交换格式, 主要被用作MongoDB数据库中的数据存储和网络传输格式。它是一种二进制表示形式,能用来表示简单数.
据结构、关联数组(MongoDB中称为“对象”或“文档”)以及MongoDB中的各种数据类型。BSON之名缘于JSON,含义为Binary JSON(二进制JSON)
| JSON | BSON |
|---|---|
JSON 是 javascript 对象表示法 |
BSON 是二进制 JSON |
| 是一种轻量级的、基于文本的、开放的数据交换格式 | 是一种二进制序列化文档格式 |
JSON 包含一些基本数据类型,如字符串、数字、布尔值、空值 |
除了支持 JSON 中的类型外,BSON 还包含一些额外的数据类型,例如日期(Date)、二进制(BinData)等 |
AnyDB、redis 等数据库将数据存储为 JSON 格式 |
MongoDB 中将数据存储为BSON 格式 |
| 主要用于传输数据 | 主要用于存储数据 |
| 没有响应的编码和解码技术 | 有专用的编码和解码技术 |
如果想从 JSON 文件中读取指定信息,需要遍历整个数据 |
在 BSON 中,可以使用索引跳过到指定内容 |
JSON 格式不需要解析,因为它是人类可读的 |
BSON 需要解析,因为它是二进制的 |
JSON 是对象和数组的组合,其中对象是键值对的集合,而数组是元素的有序列表 |
BSON 是二进制数据,在其中可以存储一些附加信息,例如字符串长度、对象类型等 |
Bson 单文档的大小及嵌套限制
- 单文档不超过16 MB
- 嵌套不能超过100 层
如果单条记录超过 16 M 怎么办?
第一种办法:先处理后存储。可以先做压缩,或者也可以对字符进行先哈希,然后再存储,这样大概率就不会超过 16 MB。
第二种方法:通常来说 16 MB 的记录都可以直接写到文本文件里面,然后再将文件存到
MongoDB GridFS里面或者先业务层处理后存储。
2.2 数据类型
| 据类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| String | 字符串。存储数据常用的数据类型。在 MongoDB 中,UTF-8 编码的字符串才是合法的。 |
| Integer | 整型数值。用于存储数值。根据你所采用的服务器,可分为 32 位或 64 位。 |
| Boolean | 布尔值。用于存储布尔值(真/假)。 |
| Double | 双精度浮点值。用于存储浮点值。 |
| Min/Max keys | 将一个值与 BSON(二进制的 JSON)元素的最低值和最高值相对比。 |
| Array | 用于将数组或列表或多个值存储为一个键。 |
| Timestamp | 时间戳。记录文档修改或添加的具体时间。 |
| Object | 用于内嵌文档。 |
| Null | 用于创建空值。 |
| Symbol | 符号, 该数据类型基本上等同于字符串类型,但不同的是,它一般用于采用特殊符号类型的语言. |
| Date | 日期时间。用 UNIX 时间格式来存储当前日期或时间。你可以指定自己的日期时间:创建 Date 对象,传入年月日信息。 |
| Object ID | 对象 ID, 用于创建文档的 ID(每个文档都有) |
| Binary Data | 二进制数据, 用于存储二进制数据 |
| Code | 代码类型, 用于在文档中存储 JavaScript 代码 |
| Regular expression | 正则表达式 |
2.3 ObjectID
ObjectIds are small, likely unique, fast to generate, and ordered. ObjectId values are 12 bytes in length, consisting of:
- A 4-byte timestamp, representing the ObjectId's creation, measured in seconds since the Unix epoch.
- A 5-byte random value generated once per process. This random value is unique to the machine and process.
- A 3-byte incrementing counter, initialized to a random value.
ObjectID是在插入数据到mongodb时默认生成的ID.
其的组成:
- 4-byte, 时间戳
- 5-byte, 随机生成数
- 3-byte, 递增数(在一个随机初始化的数开始递增)
'63ae59def83e2624ec87bb3c'.length;
// 24
三. 基本概况
3.1 Shell
We’ve decided to switch from v8 and java to Spider Monkey for JavaScript. - 官方blog
mongodb的shell整合了一个浏览器引擎(firefox, Spider Monkey).
这意味着可以直接在shell环境下执行JavaScript代码, 如同和在chrome console上.
# console.log()
'test'.length;

注: 注意执行后js代码将从控制台中移除.
// 直接在控制台执行复杂的js代码, 支持ES6+
const datas = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
const info = {
'id': i,
'name': 'abc'
}
datas.push(info);
}
// 批量插入条数据
// db.student.insertMany(datas);
实际上, mongodb和JavaScript的关系, 可以一定程度认为JavaScript是mongodb的脚本语言
// nodejs
const cursor = collection.find({});
await cursor.forEach(doc => console.log(doc));
// shell
// 创建一个游标
const mycursor = db.shop.find()
// 对游标获取的对象(obj)进行遍历(forEach)打印(printjson)
mycursor.forEach(function(obj){printjson(obj)})
注意: mongodb默认状态下, 是开放状态的, 连接是不需要密码和用户名的.
3.2 预置数据库
admin:admin数据库主要是保存root用户和角色。例如,system.users表存储用户,system.roles表存储角色。一般不建议用户直接操作这个数据库。将一个用户添加到这个数据库,且使它拥有admin库上的名为dbAdminAnyDatabase的角色权限,这个用户自动继承所有数据库的权限。一些特定的服务器端命令也只能从这个数据库运行,比如关闭服务器。local:local数据库是不会被复制到其他分片的,因此可以用来存储本地单台服务器的任意collection。一般不建议用户直接使用local库存储任何数据,也不建议进行CRUD操作,因为数据无法被正常备份与恢复。config: 当MongoDB使用分片设置时,config数据库可用来保存分片的相关信息。
3.3 创建用户/安全管理
默认状态下, 使用的是已经内置创建的test数据库
# 管理员账户
use admin
db.createUser(
{
user: "myUserAdmin",
pwd: passwordPrompt(), // or cleartext password
roles: [
{ role: "userAdminAnyDatabase", db: "admin" },
{ role: "readWriteAnyDatabase", db: "admin" }
]
}
)
# 普通账户
use test
db.createUser(
{
user: "myTester",
pwd: passwordPrompt(), // or cleartext password
roles: [ { role: "readWrite", db: "test" },
{ role: "read", db: "reporting" } ]
}
)
3.4 MySQL的对比
- 数据库, 依然还是数据库,
database - 表(
Table), 则可以认为是转换成collection - 行(row), 则可以认为转换成
document - index还是index
- 字段(column)勉强和field相对应
mongodb对于使用数据库/集合(表)的处理方式是, 当对应的数据存在时就访问, 当数据不存在时, 就临时创建, 假如不插入数据, 则临时文件会自动删除掉.
相比于MySQL需要在建库, 建表时需要各种考虑细节, mongodb可以开盖直接使用, 但是需要注意这种自由带来的数据混乱和不标准的问题.(特别是多人同时使用同一数据库时)
如果在具体执行中, 假如输入的内容错误(常见的拼写错误), 也不会报错.
例如:
这种问题也可以看到mongodb"自由"的代价.
db.students.insertMany()
# 而你的数据输入出现拼写错误或者是漏写/多写的错误, 也不会报错
db.student.insertMany()
# 将会直接创建对应名称的集合, 插入数据到这个集合
这需要在权限管理上进行限制, 以避免这种错误导致的数据混乱.
3.5 基本命令
show dbs;
# 等价于mysql语句, 但同时也支持show databases;
# mysql
show databases;
# 查看集合
show collections;
# 删除数据库, 在当前数据库, 即可删除掉数据库
db.dropDatabase()
# 删除集合
db.collection.drop()
# 清空集合, 对应的集合将会自动回收(删除)
use db_name;
# 切换使用的数据库, 和mysql一样.
由于mongodb的字段(field)是不固定结构的, 所以并没有和MySQL与之对应的概念.
show full columns from table_name;
# 查看表的字段的情况
一些常用的管理命令
# 查看数据库的情况
db.stats();
# query, 返回具体的检索文档的数量
db.collection.countDocuments({?query});
# 查看数据库连接状态
db.serverStatus().connections
# 类似于netstat命令, 查看连接的状态
# 执行语句的解析
db.student.find({'id': 1}).explain();
其他命令
# command generates a list of all database commands implemented for the current mongod or mongos instance.
# 查看所有的命令
db.listCommands();
# 运行命令
# 查找student(collection_name), 过滤掉没有name的项, 返回两个结果
db.runCommand({"find":"student","filter":{"name":{$exists:true}},"limit" : 2});
四. 其他事项
4.1 游标
The following functions directly return cursors:
返回的是游标的函数
Collection.find()Collection.aggregate()Collection.listIndexes()Db.aggregate()Db.listCollections()Other methods such as Collection.findOne() and Collection.watch() use cursors internally, and return the results of the operations instead of a cursor.
c = collection.find()
print(c)
# <pymongo.cursor.Cursor at 0x217493afb80>
# find_one() 返回的是dict or None
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| cursor.addOption() | 添加特殊的线程协议标志,用于修改查询的行为。 |
| cursor.batchSize() | 控制 MongoDB 在单个网络消息中返回客户端的文档数。 |
| cursor.close() | 关闭游标并释放相关的服务器资源。 |
| cursor.isClosed() | true 如果光标关闭则返回。 |
| cursor.collation() | 指定由返回的游标的排序规则。 |
| cursor.comment() | 在查询中附加注释,以便在日志和 system.profile 集合中实现可跟踪性。 |
| cursor.count() | 返回结果集中的文档数。 |
| cursor.explain() | 报告游标的查询执行计划。 |
| cursor.forEach() | 为游标中的每个文档应用 JavaScript 函数。 |
| cursor.hasNext() | 如果游标包含文档并且可以迭代,则返回 true。 |
| cursor.hint() | 强制 MongoDB 为查询使用特定索引。 |
| cursor.isExhausted() | 检查游标是否处于关闭状态,为 true 代表关闭。 |
| cursor.itcount() | 通过获取和迭代结果集来计算游标客户端中的文档总数。 |
| cursor.limit() | 约束游标结果集的大小。 |
| cursor.map() | 将函数应用于游标中的每个文档,并收集数组中的返回值。 |
| cursor.max() | 指定游标的独占上限索引。 |
| cursor.maxScan() | 指定要扫描的最大项目数; 收集扫描的文档,索引扫描的键。已过时 |
| cursor.maxTimeMS() | 指定处理游标操作的累积时间限制(以毫秒为单位)。 |
| cursor.min() | 指定游标的包含性较低索引范围。用于 cursor.hint() |
| cursor.next() | 返回游标中的下一个文档。 |
| cursor.noCursorTimeout() | 指示服务器在一段时间不活动后自动关闭光标。 |
| cursor.objsLeftInBatch() | 返回当前游标批处理中剩余的文档数。 |
| cursor.pretty() | 配置光标以易于阅读的格式显示结果。 |
| cursor.readConcern() | 指定读取关注的find() |
| cursor.readPref() | 指定对游标的读取首选项,以控制客户端如何将查询定向到复制集。 |
| cursor.returnKey() | 修改游标以返回索引键而不是文档。 |
| cursor.showRecordId() | 向光标返回的每个文档添加内部存储引擎ID字段。 |
| cursor.size() | 返回应用 skip() |
| cursor.skip() | 返回仅在传递或跳过多个文档后才开始返回结果的游标。 |
| cursor.sort() | 返回根据排序规范排序的结果。 |
| cursor.tailable() | 将光标标记为 tailable,仅适用于超过上限集合的游标。 |
| cursor.toArray() | 返回一个数组,其中包含游标返回的所有文档。 |
4.2 索引
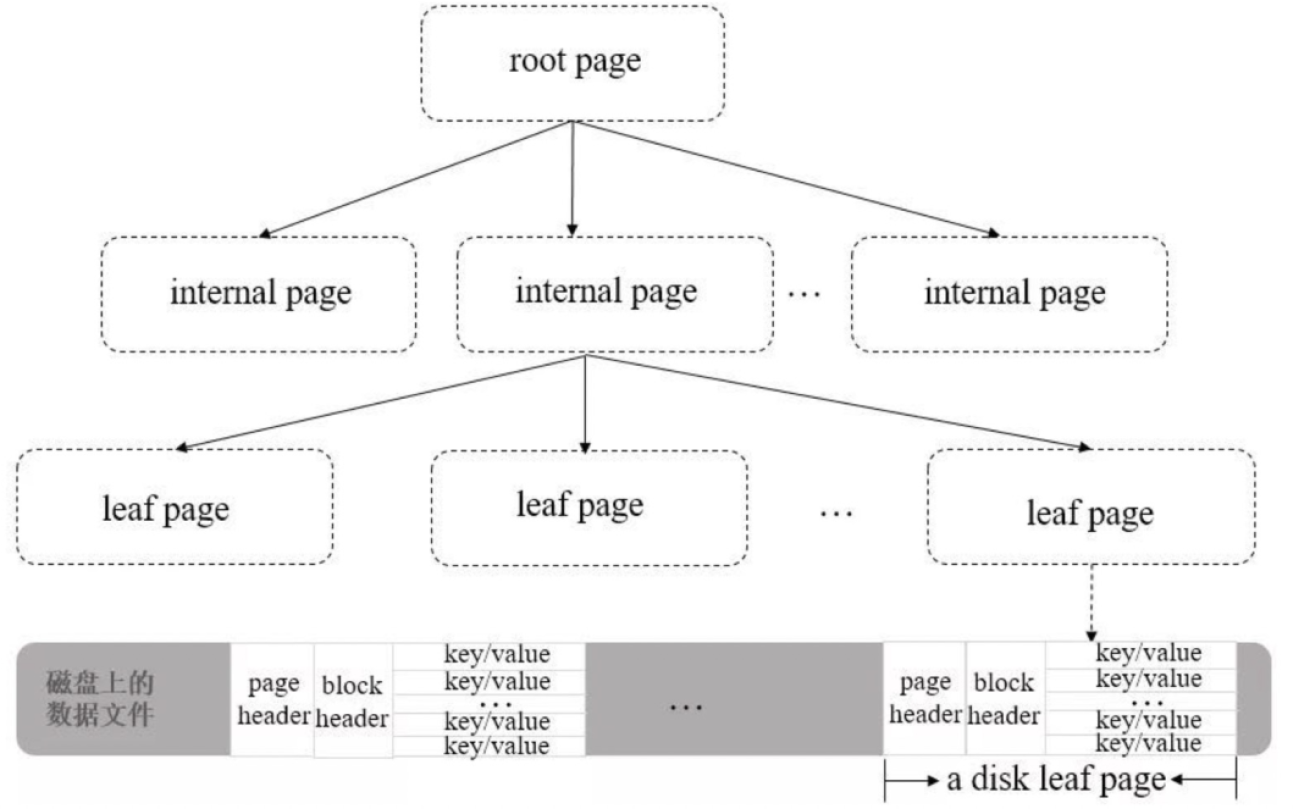
- db.collection.createIndex(keys, options, commitQuorum)
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| background | Boolean | 建索引过程会阻塞其它数据库操作,background可指定以后台方式创建索引,即增加 "background" 可选参数。 "background" 默认值为false。 |
unique |
Boolean | 建立的索引是否唯一。指定为true创建唯一索引。默认值为false. |
name |
string | 索引的名称。如果未指定,MongoDB的通过连接索引的字段名和排序顺序生成一个索引名称。 |
| dropDups | Boolean | **3.0+版本已废弃。**在建立唯一索引时是否删除重复记录,指定 true 创建唯一索引。默认值为 false. |
| sparse | Boolean | 对文档中不存在的字段数据不启用索引;这个参数需要特别注意,如果设置为true的话,在索引字段中不会查询出不包含对应字段的文档.。默认值为 false. |
| expireAfterSeconds | integer | 指定一个以秒为单位的数值,完成 TTL设定,设定集合的生存时间。 |
| v | index version | 索引的版本号。默认的索引版本取决于mongod创建索引时运行的版本。 |
weights |
document | 索引权重值,数值在 1 到 99,999 之间,表示该索引相对于其他索引字段的得分权重。 |
| default_language | string | 对于文本索引,该参数决定了停用词及词干和词器的规则的列表。 默认为英语 |
| language_override | string | 对于文本索引,该参数指定了包含在文档中的字段名,语言覆盖默认的language,默认值为 language. |
支持的索引类型
- 单个索引
- 复合索引
- 多键索引(基于数组来创建索引, 但是对于一个复合多键索引,「每个索引最多可以包含一个数组」)
- 地理空间索引(专门针对LBS信息检索的)
- 文本索引(全文检索, 不支持中文)
- Hashed索引
索引的特性
-
唯一索引(_id, 默认状态下的唯一索引)
-
部分索引(部分索引仅索引集合中符合指定过滤器表达式的文档, 如仅当某些数据大于某值时)
# children 表中,将 age 大于 5 数据创建一个升序索引 db.children.createIndex( {age:1}, {partialFilterExpression: {age: {$gt:5}}}) -
稀疏索引
索引的稀疏属性可确保索引仅包含具有索引字段的文档的条目。索引会跳过没有索引字段的文档。创建方式就是加上 sparse: true
db.children.createIndex( { "age": 1 }, { sparse: true } ) -
TTL索引(时效)
TTL 索引是 MongoDB 可以使用的特殊索引,它可以在一定时间后自动从集合中删除文档.
db.children.createIndex( { "lastModifiedDate": 1 }, { expireAfterSeconds: 5 } ) -
覆盖索引
所有需要查询的数据都在索引当中,不需要从数据页中再去寻找数据
# 简单理解, 就是索引即内容 # 比如我此时为 children 表的时间创建了一个索引 db.children.createIndex({ age : 1 }) # 在此时我查找年龄为两岁的孩子时,就不需要从数据页中去寻找数据了 db.children.find({ age : 2 }) -
前缀索引
所有的前缀索引都可以被这条索引所覆盖,不需要再去针对这些前缀建立额外的索引,避免额外的开销
比如我此时为 children 表的时间创建了「一个复合索引(多字段索引)」db.children.createIndex({ age : 1,name : 1,address : 1}) # 等价于 db.children.createIndex({ age : 1 }) db.children.createIndex({ age : 1,name : 1 }) db.children.createIndex({ age : 1,name : 1,address : 1})
常用索引命令/示例
图示: compass索引的创建
# 查看索引
db.student.getIndexes();
# 默认带有的索引是 "_id", 即数据库自带的
# 查看索引的大小
db.student.totalIndexSize();
# 删除所有的index
db.col.dropIndexes();
# 删除指定的索引
db.col.dropIndex("index_name")
# 创建单个索引
db.collection.createIndex({ id : 1 })
# 复合索引
db.collection.createIndex({ id : 1,name : 1 })
# 多键索引
db.collection.createIndex({"grades:math":1})
# ------------------------------------------------------- #
db.testindex2.insertMany([
{ id: 5, type: "food", item: "aaa", ratings: [ 5, 8, 9 ] },
{ id: 6, type: "food", item: "bbb", ratings: [ 5, 9 ] },
{ id: 7, type: "food", item: "ccc", ratings: [ 9, 5, 8 ] },
{ id: 8, type: "food", item: "ddd", ratings: [ 9, 5 ] },
{ id: 9, type: "food", item: "eee", ratings: [ 5, 9, 5 ] }
]);
下面基于ratings列创建一个多键索引:
db.testindex2.createIndex( { ratings: 1 } );
查询数组上为5, 9的文档
db.testindex2.find( { ratings: [ 5, 9 ] } );
下面查看其执行计划
db.testindex2.find( { ratings: [ 5, 9 ] } ).explain();
# 注意关键字: 「stage 为 IXSCAN」
{
explainVersion: '1',
queryPlanner: {
namespace: 'test_db.testindex2',
indexFilterSet: false,
parsedQuery: { ratings: { '$eq': [ 5, 9 ] } },
queryHash: 'E0BF65C3',
planCacheKey: '2FB9799A',
maxIndexedOrSolutionsReached: false,
maxIndexedAndSolutionsReached: false,
maxScansToExplodeReached: false,
winningPlan: {
stage: 'FETCH',
filter: { ratings: { '$eq': [ 5, 9 ] } },
inputStage: {
stage: 'IXSCAN',
keyPattern: { ratings: 1 },
indexName: 'ratings_1',
isMultiKey: true,
multiKeyPaths: { ratings: [ 'ratings' ] },
isUnique: false,
isSparse: false,
isPartial: false,
indexVersion: 2,
direction: 'forward',
indexBounds: { ratings: [ '[5, 5]', '[[ 5, 9 ], [ 5, 9 ]]' ] }
}
},
rejectedPlans: []
},
command: {
find: 'testindex2',
filter: { ratings: [ 5, 9 ] },
'$db': 'test_db'
},
serverInfo: {
host: 'DESKTOP-F6VO5U4',
port: 27017,
version: '6.0.2',
gitVersion: '94fb7dfc8b974f1f5343e7ea394d0d9deedba50e'
},
serverParameters: {
internalQueryFacetBufferSizeBytes: 104857600,
internalQueryFacetMaxOutputDocSizeBytes: 104857600,
internalLookupStageIntermediateDocumentMaxSizeBytes: 104857600,
internalDocumentSourceGroupMaxMemoryBytes: 104857600,
internalQueryMaxBlockingSortMemoryUsageBytes: 104857600,
internalQueryProhibitBlockingMergeOnMongoS: 0,
internalQueryMaxAddToSetBytes: 104857600,
internalDocumentSourceSetWindowFieldsMaxMemoryBytes: 104857600
},
ok: 1
}
4.2.1 索引的解析
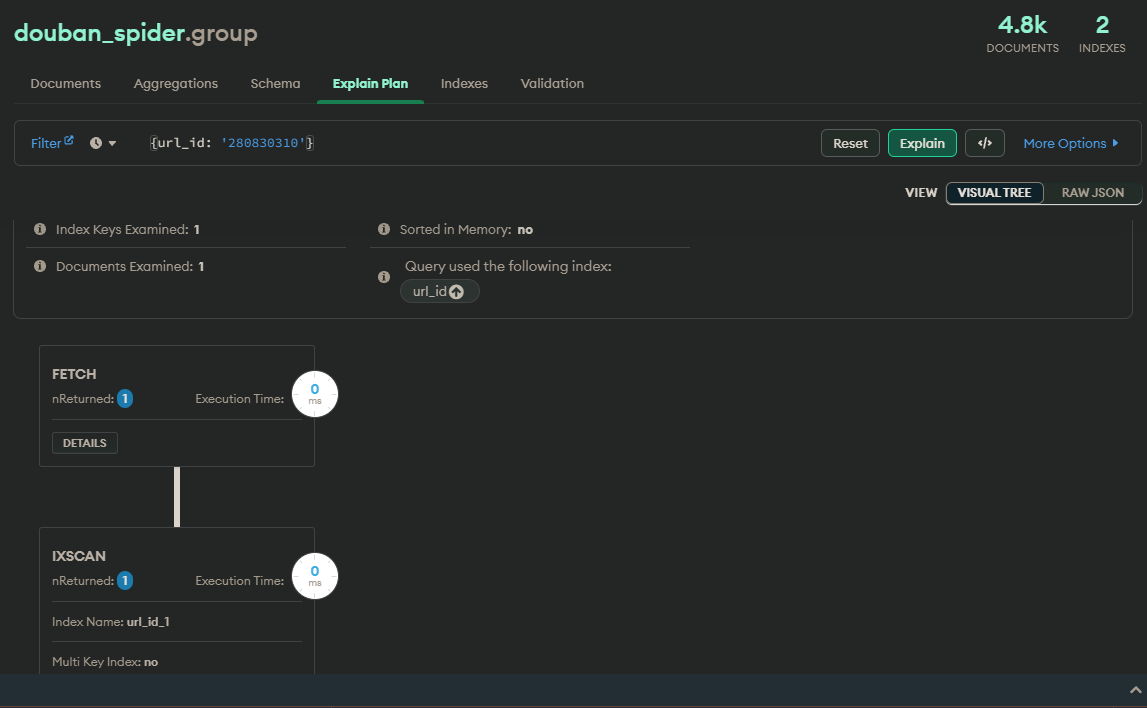
图示: compass中的explain执行
常见的explain的内容解析
| 状态 | 描述 |
|---|---|
COLLSCAN |
全表扫描 |
IXSCAN |
索引扫描 |
FETCH |
根据索引检索指定文档 |
SHARD_MERGE |
将各个分片返回数据进行合并 |
SORT |
在内存中进行了排序 |
LIMIT |
使用limit限制返回数 |
SKIP |
使用skip进行跳过 |
IDHACK |
对_id进行查询 |
SHARDING_FILTER |
通过mongos对分片数据进行查询 |
COUNTSCAN |
count不使用Index进行count时的stage返回 |
COUNT_SCAN |
count使用了Index进行count时的stage返回 |
SUBPLA |
未使用到索引的$or查询的stage返回 |
TEXT |
使用全文索引进行查询时候的stage返回 |
PROJECTION |
限定返回字段时候stage的返回 |
4.2.2 全文索引
需要注意的是全文索引, 并不支持中文
| Language Name | ISO 639-1 (Two letter codes) |
|---|---|
danish |
da |
dutch |
nl |
english |
en |
finnish |
fi |
french |
fr |
german |
de |
hungarian |
hu |
italian |
it |
norwegian |
nb |
portuguese |
pt |
romanian |
ro |
russian |
ru |
spanish |
es |
swedish |
sv |
turkish |
tr |
指定语言为全文索引
db.quotes.createIndex(
{ content : "text" },
{ default_language: "spanish" }
)
对于中文全文检索有较高要求的, 备用选择, MongoDB和Elasticsearch的各使用场景对比
| MongoDB | ElasticSearch | 备注 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 定位 | (文档型)数据库 | (文档型)搜索引擎 | 一个管理数据,一个检索数据 |
| 资源占用 | 一般 | 高 | mongo使用c++, es使用Java开发 |
| 写入延迟 | 低 | 高 | es的写入延迟默认1s, 可配置, 但是要牺牲一些东西 |
| 全文索引支持度 | 一般 | 非常好 | es本来就是搜索引擎, 这个没啥可比性 |
| 有无Schema | 无 | 无 | 两者都是无Schema |
| 支持的数据量 | PB+ | TB+ ~ PB | 两者支持的量并不好说的太死, 都支持分片和横向扩展, 但是相对来说MongoDB的数据量支持要更大一点 |
| 性能 | 非常好 | 好 | MongoDB在大部分场景性能比es强的多得多 |
| 索引结构 | B树 | LSM树 | es追求写入吞吐量, MongoDB读写比较均衡 |
| 操作接口 | TCP | Restful(Http) | |
| 是否支持分片 | 是 | 是 | |
| 是否支持副本 | 是 | 是 | |
| 选主算法 | Bully(霸凌) | Bully(霸凌) | 相比于Paxos和Raft算法实现更简单并有一定可靠性上的妥协,但是选举速度比较快 |
| 扩展难度 | 容易 | 非常容易 | es真的是我用过的扩展最方便的存储系统之一 |
| 配置难度 | 难 | 非常容易 | |
| 地理位置 | 支持 | 支持 | |
| 运维工具 | 丰富 | 一般 | |
| 插件和引擎 | 有多个存储引擎供选择 | 有大量插件可以使用 | - |
4.2.3 索引限制
-
单个集合最多包含 64 个索引
-
单个索引记录不超过 1024 字节,
failIndexKeyTooLong默认true控制是否报错 -
多列索引列个数最多不超过 31
-
前台模式 createIndexes内存限制500 MB,(
maxIndexBuildMemoryUsageMegabytes可调整) -
不允许创建多列数组的组合索引
实际上为什么有这个限制呢?
MongoDB 如果索引字段是数组,那我们可以理解为对每个数组元素创建索引。如果要是多个数组字段建组合索引,就意味着它可能会产生笛卡尔级数据量的索引。所以为了避免这种索引的爆炸性增长,需要对此做了相应的一个限制。
- TTL 索引如果是复合索引则过期将会失效
通常你想创建一个 TTL 索引,但创建的时候构建了多个字段的组合索引,那么 TTL 就会失效。
- Hash 索引只支持单列 [version <= 4.4]
另外需要记住的就是哈希索引只支持单例,这个是在
4.4之前的一个限制,到后面是做了调整,所以在这里也需要给大家提一下。我们本次分享为大部分内容的前提是小于等于4.2版本,主要原因在于4.4及其以上的MongoDB版本其实有很多企业里面都没有使用。
4.3 时间
ISODate("2019-07-26T16:55:36.000Z")
时间在插入数据库后, 相应的时区会被修改为UTC00:00(Z)
# 在python中直接将字符串转为datetime
student = {
'id': '2017010x',
'name': 'Jordap',
'age': 21,
'gender': 'male',
'data': datetime.strptime('2022-12-27 14:29:26', '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
}
# 插入后检索数据
test_db> db.students.findOne({'id': '2017010x'});
{
_id: ObjectId("63aaae7b995a3a30dffe2a7d"),
id: '2017010x',
name: 'Jordap',
age: 21,
gender: 'male',
data: ISODate("2022-12-27T14:29:26.000Z")
}
# 注意日期
# 在pymongo中将数据导出
{'_id': ObjectId('63aaae7b995a3a30dffe2a7d'), 'id': '2017010x', 'name': 'Jordap', 'age': 21, 'gender': 'male', 'data': datetime.datetime(2022, 12, 27, 14, 29, 26)}
# 返回的date对象是不带有时区信息的
4.4 $操作符
The positional
$operator limits the contents of an<array>to return the first element that matches the query condition on the array.Use$in the projection document of thefind()method or thefindOne()method when you only need one particular array element in selected documents.See the aggregation operator$filterto return an array with only those elements that match the specified condition.
4.5 高阶操作
-
事务
For transactions:
-
You can specify read/write (CRUD) operations on existing collections. For a list of CRUD operations, see CRUD Operations.
-
Starting in MongoDB 4.4, you can create collections and indexes in transactions. For details, see Create Collections and Indexes In a Transaction
-
The collections used in a transaction can be in different databases.
NOTE
You cannot create new collections in cross-shard write transactions. For example, if you write to an existing collection in one shard and implicitly create a collection in a different shard, MongoDB cannot perform both operations in the same transaction.
-
You cannot write to capped collections. (Starting in MongoDB 4.2)
-
You cannot use read concern
"snapshot"when reading from a capped collection. (Starting in MongoDB 5.0) -
You cannot read/write to collections in the
config,admin, orlocaldatabases. -
You cannot write to
system.*collections. -
You cannot return the supported operation's query plan (i.e.
explain). -
For cursors created outside of a transaction, you cannot call
getMoreinside the transaction. -
For cursors created in a transaction, you cannot call
getMoreoutside the transaction. -
Starting in MongoDB 4.2, you cannot specify
killCursorsas the first operation in a transaction.
Operations that affect the database catalog, such as creating or dropping a collection or an index, are not allowed in multi-document transactions. For example, a multi-document transaction cannot include an insert operati
-
-
连表查询
和MySQL不同的是,
mongodb并无联表查询的概念(提供有$lookup操作符来实现类似功能), 多是采用内嵌文档的方式实现. -
分片
在Mongodb里面存在另一种集群,就是分片技术,可以满足MongoDB数据量大量增长的需求。
当MongoDB存储海量的数据时,一台机器可能不足以存储数据,也可能不足以提供可接受的读写吞吐量。这时,我们就可以通过在多台机器上分割数据,使得数据库系统能存储和处理更多的数据。
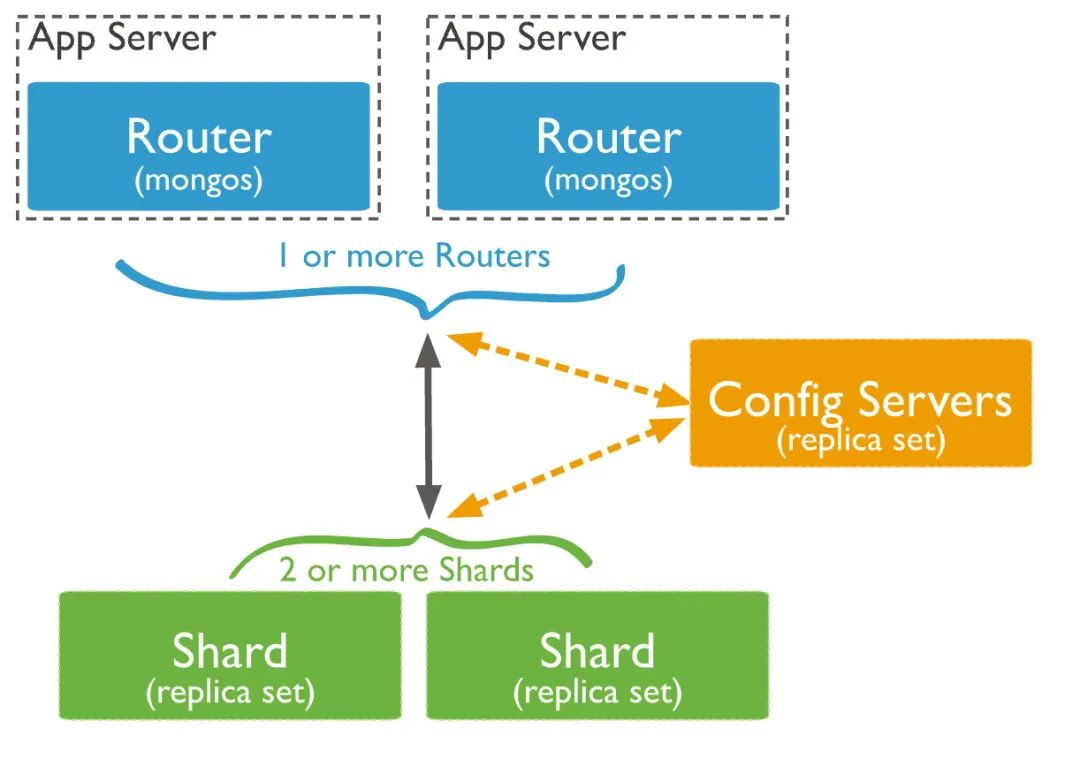
-
Shard:
用于存储实际的数据块,实际生产环境中一个shard server角色可由几台机器组个一个replica set承担,防止主机单点故障
-
Config Server:
mongod实例,存储了整个 ClusterMetadata,其中包括 chunk信息。
-
Query Routers:
前端路由,客户端由此接入,且让整个集群看上去像单一数据库,前端应用可以透明使用。
-
五. 基本操作
mongodb在API接口上一般提供: 操作单个(One)文档; 操作多个(Many)文档. 在操作上直接做了区分, 更为方便易用.
5.1 增
- insertOne
- insertMany
# 单一内容插入
db.collection.insertOne({'id': 1, 'name': 'alex'})
# 批量插入内容
db.collection.insertMany([{'id': 1, 'name': 'alex'}, {'id': 2, 'name': 'tom'}])
5.2 删
- deleteOne
- deleteMany
# 批量删除id小于5的内容
db.student.deleteMany({"id":{$lt:5}});
5.3 改
db.collection.updateOne(filter,update,options)
| 参数 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| filter | 文献 | 更新的选择标准。提供与方法中相同的查询选择器find()。指定一个空文档以更新集合中返回的第一个文档。{ } |
| update | 文件或管道 | 要应用的修改。可以是以下之一:更新文件仅包含更新运算符表达式。有关更多信息,请参见 使用更新运算符表达式文档进行更新。聚合管道 (从MongoDB 4.2开始)仅包含以下聚合阶段:$addFields 及其别名 $set$project 及其别名 $unset$replaceRoot及其别名$replaceWith。有关更多信息,请参见 使用聚合管道更新。要使用替换文档进行更新,请参阅 db.collection.replaceOne()。 |
upsert |
布尔值 | 可选的。当true,updateOne()要么:如果没有文档与匹配,则创建一个新文档filter。有关更多详细信息,请参见upsert行为。更新与匹配的单个文档filter。为避免多次更新,请确保filter字段被唯一索引。默认为false。 |
writeConcern |
文献 | 可选的。表达书面关切的文件。省略使用默认的写关注。如果在事务中运行,则不要为操作明确设置写关注点。要对事务使用写关注,请参见 事务和写关注。 |
collation |
文献 | 可选的。指定 用于操作的排序规则。归类允许用户为字符串比较指定特定于语言的规则,例如字母大写和重音符号的规则。排序规则选项具有以下语法:collation: { locale: <string>, caseLevel: <boolean>, caseFirst: <string>, strength: <int>, numericOrdering: <boolean>, alternate: <string>, maxVariable: <string>, backwards: <boolean> } 指定排序规则时,该locale字段为必填字段;所有其他排序规则字段都是可选的。有关字段的说明,请参见整理文档。如果未指定排序规则,但是集合具有默认排序规则(请参阅参考资料db.createCollection()),则该操作将使用为集合指定的排序规则。如果没有为集合或操作指定排序规则,则MongoDB使用先前版本中使用的简单二进制比较进行字符串比较。您不能为一个操作指定多个排序规则。例如,您不能为每个字段指定不同的排序规则,或者如果对排序执行查找,则不能对查找使用一种排序规则,而对排序使用另一种排序规则。3.4版的新功能。 |
arrayFilters |
数组 | 可选的。筛选器文档数组,用于确定要对数组字段进行更新操作要修改的数组元素。在更新文档中,使用$[\]过滤后的位置运算符定义一个标识符,然后在数组过滤器文档中引用该标识符。如果该标识符未包含在更新文档中,则不能具有标识符的数组过滤器文档。注意在<identifier>必须以小写字母开头,并且只包含字母数字字符。您可以在更新文档中多次包含相同的标识符;但是,对于$[identifier]更新文档中的每个不同的标识符(),必须精确地指定一个 对应的数组过滤器文档。也就是说,您不能为同一标识符指定多个数组过滤器文档。例如,如果update语句包含标识符x (可能多次),则不能为以下内容指定以下内容 arrayFilters:包括2个单独的过滤器文档x:// INVALID [ { "x.a": { $gt: 85 } }, { "x.b": { $gt: 80 } } ] 但是,您可以在单个过滤器文档中的相同标识符上指定复合条件,例如以下示例:// Example 1 [ { $or: [{"x.a": {$gt: 85}}, {"x.b": {$gt: 80}}] } ] // Example 2 [ { $and: [{"x.a": {$gt: 85}}, {"x.b": {$gt: 80}}] } ] // Example 3 [ { "x.a": { $gt: 85 }, "x.b": { $gt: 80 } } ] 有关示例,请参阅为数组更新操作指定arrayFilters。3.6版的新功能。 |
| hint | 文件或字串 | 可选的。指定用于支持查询谓词的索引的文档或字符串。该选项可以采用索引规范文档或索引名称字符串。如果指定的索引不存在,则操作错误。有关示例,请参阅为更新操作指定提示。4.2.1版中的新功能。 |
- update
- updateOne
- replacceOne
db.student.updateOne({"id": 11}, {"gender" : "female"});
# MongoInvalidArgumentError: Update document requires atomic operators
mongodb为了防止意外的修改, 不允许直接覆盖式更新(上述内容可能只是想更新其中某个字段, 但是却会导致这个部分的文档被覆盖新的内容).
假如需要真的执行对文档的覆盖更新, 使用的式replaceOne
- 操作符,
$set
# 整个文档覆盖更新
db.student.replaceOne({"id": 11}, {"gender" : "female"});
# 只更更新其中的项
db.student.updateOne({'id': 6}, {$set: {'name': 'alex'}});
- 操作符, $setOnInsert
$setOnInsert当数据不存在则写入, 当数据存在则不操作.
# 数据存在则更新, 不存在则写入
db.student.updateOne({'id': 7}, {$set: {'name': 'alex'}}, { upsert: true });
db.student.updateOne(
{ id: 31 },
{
$set: { item: "apple" },
$setOnInsert: { defaultQty: 100 }
},
{ upsert: true }
);
db.student.updateOne(
{ id: 31 },
{
$set: { item: "meta" },
$setOnInsert: { defaultQty: 120 }
},
{ upsert: true }
);
5.4 查
5.4.1 简单查询
- find
- findOne
- limit
- skip
# 返回id对应的所有项
db.collection_name.find({'id': 12345});
# 返回一条结果
db.collection_name.findOne({'id': 12345});
# 等价于
db.collection_name.find({'id': 12345}).limit(1);
# 只展示部分的字段, url_id
db.group.find({}, {'url_id': true});
# 展示除了url_id之外的其他的所有字段
db.group.find({}, {'url_id': false});
# 排序
# 查找具体项的最大值
# 不限于数字, 日期也可以
db.group.find().sort({'commentCount': -1}).limit(1)
# -1, 逆序
# 1, 正序
# 返回author_id的独一无二值
# db.collection.distinct(field, query, options)
db.group.distinct('author_id');
# 注意错误
# Error: distinct too big, 16mb cap
db.group.distinct('comments.author_id', {'url_id': '280793330'});
5.4.2 type
$type操作符是基于BSON类型来检索集合中匹配的数据类型,并返回结果。
| 类型 | 数字 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| Double | 1 | |
| String | 2 | |
| Object | 3 | |
| Array | 4 | |
| Binary data | 5 | |
| Undefined | 6 | 已废弃 |
| Object id | 7 | |
| Boolean | 8 | |
| Date | 9 | |
| Null | 10 | |
| Regular Expression | 11 | |
| JavaScript | 13 | |
| Symbol | 14 | |
| JavaScript (with scope) | 15 | |
| 32-bit integer | 16 | |
| Timestamp | 17 | |
| 64-bit integer | 18 | |
| Min key | 255 | Query with -1. |
| Max key | 127 |
# 返回gender中数据类型为string的项
db.student.find({'gender': {$type: 2}})
5.4.3 条件(数学)操作符
| 操作 | 格式 | 范例 | RDBMS中的类似语句 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 等于 | {<key>:<value>} |
db.col.find({"by":"google"}).pretty() |
where by = 'google' |
| 小于 | {<key>:{$lt:<value>}} |
db.col.find({"likes":{$lt:50}}).pretty() |
where likes < 50 |
| 小于或等于 | {<key>:{$lte:<value>}} |
db.col.find({"likes":{$lte:50}}).pretty() |
where likes <= 50 |
| 大于 | {<key>:{$gt:<value>}} |
db.col.find({"likes":{$gt:50}}).pretty() |
where likes > 50 |
| 大于或等于 | {<key>:{$gte:<value>}} |
db.col.find({"likes":{$gte:50}}).pretty() |
where likes >= 50 |
| 不等于 | {<key>:{$ne:<value>}} |
db.col.find({"likes":{$ne:50}}).pretty() |
where likes != 50 |
{
_id: ObjectId("63ac018e8ec05aca7ba5c922"),
id: 10,
name: 'tony',
grades: { math: 12, english: 10 }
}
# 嵌套了一个字典层级
# 查找math下等于12的项目
db.student.findOne({'grades.math': 12});
# 查找math小于20的项目
db.student.find({'grades.math': {$lt: 20}});
5.4.4 复杂查询
常见操作符
| 符号 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| $all | {"name":{$all: ["piexl", "tom"]}}, 满足["piexl", "tom"]内全部内容的 |
| $or | {$or: [{'url_id':'102117210'}, {'url_id': '280826584'}]}, 下面的in语句的or版本, 二者是等价的 |
| $in | {'url_id': {$in: ['102117210', '280826584']}}, url_id等于包含的项的 |
| $inc | db.student.updateOne({"id": 1}, {$inc: {"id": 10}});, 对id这个数值 + 10 |
| $set | 设置值, db.student.updateOne({'id': 6}, {$set: {'name': 'alex'}}); |
| $unset | db.student.updateOne({"id": 11}, {$unset: {"name": ""}}); 删除掉id为11下的name项 |
| $push | db.student.updateOne({"id": 1}, {push: {"name": "james"}});, 在id为1的项下的name数组中, 增加一项, 需要区分重复值, 可以使用addToSet |
| $pull | db.student.updateOne({"id": 2}, {pull: {"name": "tom", "year":45}}); 删除掉对应的项, 不支持直接使用数组[45, 23]这种模式, 需要加上in: [45, 23] |
| $pop | db.student.updateOne({"id": 3}, {$pop: {"name": 1, "year":-1}});, 删除掉对应数组的第一项(-1)或者最后一项(1) |
| $max | db.student.updateOne({"id": 6}, {$max: {"id": 11}}); 假如11大于对应的项, 则设置该值为11 |
| $min | db.student.updateOne({"id": 6}, {$min: {"id": 0}});假如0小于对应的项, 则设置该值为0 |
| $nin | {id: {$nin: [3, 4]}}, id不在[3, 4]这两项的项 |
| $not | {id: {not: {lt: 4}}}, 返回id大于等于4的项 |
| $nor | {nor: [{'gender': 'male'}, {"id": {lt: 2}}]}, 返回gender不是male and 大于或等于2的项 |
| $exists | {city: {$exists: true}}, 返回存在的字段的项 |
| $size | {'name': {$size: 2}}, 返回name项下, 数组大小为2的项 |
| $eleMatch | {"year": {elemMatch: {gt: 20, $lt: 80}}}, 返回数组满足要求的数据 |
| $where | 支持传入函数(function)的方式来执行复杂的检索. {$where: "this.id > 3"}, 筛选id编号大于3的项目; 注意执行的效率问题 |
| $mod | {'id': {$mod: [3, 1]}}, 取模操作, 取 id mode 3 === 1的项 |
| $text | db.textIndexTest.find({text:{search:"李"}}) , 注意索引不支持中文 |
| $regex | {gender: {$regex: /.+male/}}, 正则表达式 |
| $slice | 对返回的数组内容进行切片, db.student.find({"id":2}, {'name': {$slice: 1}});只返回name下的第一个元素 |
| $rename | db.student.updateOne({"id": 11}, {$rename: {'grades': 'scores'}}); 对字段进行重命名 |
# 查找多个项目
db.group.find({'url_id': {$in: ['102117210', '280826584']}})
# where
# 执行复杂的语句判断, 速度可能会受到影响
# 先判断name是否存在, 存在, 则返回name数组长度大于1的项
# 但是需要注意的是, 由于js中, 存在length属性的项并不止于数组, 字符串同样也有length,
# 所以这种判断会同时返回满足要求的数据, 需要判断是否为数组isArray()
db.student.find({'name': {'$exists':true}, '$where':'this.name.length>=1'});
5.5 聚合
pipeline, 顾名思义, 管道, 数据通过在管道中逐级传递, 层层对数据进行处理, 用于返回需要经过复杂处理的数据.
注: pipeline的概念使用非常广泛, 如powerhell.
# 跳过前面2个文档
db.sales.aggregate({ $skip: 2 });
# 等价于
db.sales.find().skip(2);
# 相类似的
db.sales.find().limit(2);
# 等价于
db.sales.aggregate({ $limit: 2});
5.5.1 条件表达运算符
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| $cond | 对一个表达式求值的三元运算符,并根据结果返回另外两个表达式之一的值。接受有序列表中的三个表达式或三个命名参数。 |
| $ifNull | 返回第一个表达式的非空结果,如果第一个表达式的结果为空,则返回第二个表达式的结果。Null结果包含未定义值或缺少字段的实例。接受两个表达式作为参数。第二个表达式的结果可以为null. |
| $switch | 计算一系列用例表达。当它找到一个计算结果为true的表达式时,$switch执行一个指定的表达式并跳出控制流。 |
5.5.2 阶段操作符
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
$addFields |
Adds new fields to documents. Similar to $project, $addFields reshapes each document in the stream; specifically, by adding new fields to output documents that contain both the existing fields from the input documents and the newly added fields.$set is an alias for $addFields. |
$bucket |
Categorizes incoming documents into groups, called buckets, based on a specified expression and bucket boundaries. |
$bucketAuto |
Categorizes incoming documents into a specific number of groups, called buckets, based on a specified expression. Bucket boundaries are automatically determined in an attempt to evenly distribute the documents into the specified number of buckets. |
$changeStream |
Returns a Change Stream cursor for the collection. This stage can only occur once in an aggregation pipeline and it must occur as the first stage. |
$collStats |
Returns statistics regarding a collection or view. |
$count |
Returns a count of the number of documents at this stage of the aggregation pipeline.Distinct from the $count aggregation accumulator. |
$densify |
Creates new documents in a sequence of documents where certain values in a field are missing. |
$documents |
Returns literal documents from input expressions. |
$facet |
Processes multiple aggregation pipelines within a single stage on the same set of input documents. Enables the creation of multi-faceted aggregations capable of characterizing data across multiple dimensions, or facets, in a single stage. |
$fill |
Populates null and missing field values within documents. |
$geoNear |
Returns an ordered stream of documents based on the proximity to a geospatial point. Incorporates the functionality of $match, $sort, and $limit for geospatial data. The output documents include an additional distance field and can include a location identifier field. |
$graphLookup |
Performs a recursive search on a collection. To each output document, adds a new array field that contains the traversal results of the recursive search for that document. |
$group |
Groups input documents by a specified identifier expression and applies the accumulator expression(s), if specified, to each group. Consumes all input documents and outputs one document per each distinct group. The output documents only contain the identifier field and, if specified, accumulated fields. |
$indexStats |
Returns statistics regarding the use of each index for the collection. |
$limit |
Passes the first n documents unmodified to the pipeline where n is the specified limit. For each input document, outputs either one document (for the first n documents) or zero documents (after the first n documents). |
$listSessions |
Lists all sessions that have been active long enough to propagate to the system.sessions collection. |
$lookup |
Performs a left outer join to another collection in the same database to filter in documents from the "joined" collection for processing. |
$match |
Filters the document stream to allow only matching documents to pass unmodified into the next pipeline stage. $match uses standard MongoDB queries. For each input document, outputs either one document (a match) or zero documents (no match). |
$merge |
Writes the resulting documents of the aggregation pipeline to a collection. The stage can incorporate (insert new documents, merge documents, replace documents, keep existing documents, fail the operation, process documents with a custom update pipeline) the results into an output collection. To use the $merge stage, it must be the last stage in the pipeline.New in version 4.2. |
$out |
Writes the resulting documents of the aggregation pipeline to a collection. To use the $out stage, it must be the last stage in the pipeline. |
$planCacheStats |
Returns plan cache information for a collection. |
$project |
Reshapes each document in the stream, such as by adding new fields or removing existing fields. For each input document, outputs one document.See also $unset for removing existing fields. |
$redact |
Reshapes each document in the stream by restricting the content for each document based on information stored in the documents themselves. Incorporates the functionality of $project and $match. Can be used to implement field level redaction. For each input document, outputs either one or zero documents. |
$replaceRoot |
Replaces a document with the specified embedded document. The operation replaces all existing fields in the input document, including the _id field. Specify a document embedded in the input document to promote the embedded document to the top level.$replaceWith is an alias for $replaceRoot stage. |
$replaceWith |
Replaces a document with the specified embedded document. The operation replaces all existing fields in the input document, including the _id field. Specify a document embedded in the input document to promote the embedded document to the top level.$replaceWith is an alias for $replaceRoot stage. |
$sample |
Randomly selects the specified number of documents from its input. |
$search |
Performs a full-text search of the field or fields in an Atlas collection.NOTE$search is only available for MongoDB Atlas clusters, and is not available for self-managed deployments. To learn more, see Atlas Search Aggregation Pipeline Stages. |
$searchMeta |
Returns different types of metadata result documents for the Atlas Search query against an Atlas collection.NOTE$searchMeta is only available for MongoDB Atlas clusters running MongoDB v4.4.9 or higher, and is not available for self-managed deployments. To learn more, see Atlas Search Aggregation Pipeline Stages. |
$set |
Adds new fields to documents. Similar to $project, $set reshapes each document in the stream; specifically, by adding new fields to output documents that contain both the existing fields from the input documents and the newly added fields.$set is an alias for $addFields stage.(注意这里, 二者等价) |
$setWindowFields |
Groups documents into windows and applies one or more operators to the documents in each window.New in version 5.0. |
$skip |
Skips the first n documents where n is the specified skip number and passes the remaining documents unmodified to the pipeline. For each input document, outputs either zero documents (for the first n documents) or one document (if after the first n documents). |
$sort |
Reorders the document stream by a specified sort key. Only the order changes; the documents remain unmodified. For each input document, outputs one document. |
$sortByCount |
Groups incoming documents based on the value of a specified expression, then computes the count of documents in each distinct group. |
$unionWith |
Performs a union of two collections; i.e. combines pipeline results from two collections into a single result set.New in version 4.4. |
$unset |
Removes/excludes fields from documents.$unset is an alias for $project stage that removes fields. |
$unwind |
Deconstructs an array field from the input documents to output a document for each element. Each output document replaces the array with an element value. For each input document, outputs n documents where n is the number of array elements and can be zero for an empty array. |
5.5.3 $project
Passes along the documents with the requested fields to the next stage in the pipeline. The specified fields can be existing fields from the input documents or newly computed fields.
管道操作符, 用于传递字段的数据到下一环节
# 对返回结果的字段名称进行修改
db.students.aggregate([{ "$project": { "学生名称": "$name", "age": 1 }}]);
# $name, 在数据库中的字段的名称, name => 学生名称
[
{
_id: ObjectId("63a9585765f3c97e328cc915"),
age: 20,
'学生名称': 'Jordan'
},
{
_id: ObjectId("63aaae7b995a3a30dffe2a7d"),
age: 21,
'学生名称': 'Jordap'
}
]
# 控制返回的结果内容
db.students.aggregate([{ "$project": { "age": 1 }}]);
# 将默认的_id字段也清除掉
db.students.aggregate([{ "$project": { "age": 1, '_id': 0 }}]);
# 等价于
db.students.find({}, { "age": 1, '_id': 0 });
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
test_db> db.sales.insertMany([
... { "id" : 1, "item" : "abc", "price" : 10, "quantity" : 2, "date" : ISODate("2014-03-01T08:00:00Z") },
... { "id" : 2, "item" : "jkl", "price" : 20, "quantity" : 1, "date" : ISODate("2014-03-01T09:00:00Z") },
... { "id" : 3, "item" : "xyz", "price" : 5, "quantity" : 10, "date" : ISODate("2014-03-15T09:00:00Z") },
... { "id" : 4, "item" : "xyz", "price" : 5, "quantity" : 20, "date" : ISODate("2014-04-04T11:21:39.736Z") },
... { "id" : 5, "item" : "abc", "price" : 10, "quantity" : 10, "date" : ISODate("2014-04-04T21:23:13.331Z") }
... ]);
# $multiply, 乘积
db.sales.aggregate([{ $project : { "id": 0, "item" : 1 , "price" : 1, "quantity": {"qty" : { "$multiply" :
["$quantity", 2] }} } }]);
# 注意这里出现的错误
# Invalid $project :: caused by :: Cannot do inclusion on field item in exclusion projection
# 没有开启_id:false,默认会生成ObjectId格式的_id,把0赋值给它会出错
# 没问题
db.sales.aggregate([{ $project : { "id": 1, "item" : 1 , "price" : 1, "quantity": {"qty" : { "$multiply" :
["$quantity", 2] }} } }]);
# 没问题
# qyt只是嵌套了别名
db.sales.aggregate([{ $project : { "_id": 0, "item" : 1 , "price" : 1, "quantity": {"qty" : { "$multiply" : ["$quantity", 2] }} } }]);
[
{ item: 'abc', price: 10, quantity: { qty: 4 } },
{ item: 'jkl', price: 20, quantity: { qty: 2 } },
{ item: 'xyz', price: 5, quantity: { qty: 20 } },
{ item: 'xyz', price: 5, quantity: { qty: 40 } },
{ item: 'abc', price: 10, quantity: { qty: 20 } }
]
db.sales.aggregate([{ $project : { "_id": 0, "item" : 1 , "price" : 1, "quantity": {"$multiply" : ["$quantity", 2] } } }]);
[
{ item: 'abc', price: 10, quantity: 4 },
{ item: 'jkl', price: 20, quantity: 2 },
{ item: 'xyz', price: 5, quantity: 20 },
{ item: 'xyz', price: 5, quantity: 40 },
{ item: 'abc', price: 10, quantity: 20 }
]
# total, 对返回字段重命名
db.sales.aggregate([{ $project : { "_id": 0, "item" : 1 , "price" : 1, "total": {"$multiply" : ["$quantity", 2] } } }]);
# 对 ["$quantity", "$price"] 两个字段进行运算
db.sales.aggregate([{ $project : { "_id": 0, "item" : 1 , "price" : 1, "total": {"$multiply" : ["$quantity", "$price"] } } }]);
5.5.4 其他操作示例
| 表达式 | 描述 | 实例 |
|---|---|---|
| $sum | 计算总和。 | db.mycol.aggregate([{group : {_id : "by_user", num_tutorial : {likes"}}}]) |
| $avg | 计算平均值 | db.mycol.aggregate([{group : {_id : "by_user", num_tutorial : {likes"}}}]) |
| $min | 获取集合中所有文档对应值得最小值。aggre | db.mycol.aggregate([{group : {_id : "by_user", num_tutorial : {likes"}}}]) |
| $max | 获取集合中所有文档对应值得最大值。 | db.mycol.aggregate([{group : {_id : "by_user", num_tutorial : {likes"}}}]) |
| $push | 将值加入一个数组中,不会判断是否有重复的值。 | db.mycol.aggregate([{group : {_id : "by_user", url : {url"}}}]) |
| $addToSet | 将值加入一个数组中,会判断是否有重复的值,若相同的值在数组中已经存在了,则不加入。 | db.mycol.aggregate([{group : {_id : "by_user", url : {url"}}}]) |
| $first | 根据资源文档的排序获取第一个文档数据。 | db.mycol.aggregate([{group : {_id : "by_user", first_url : {url"}}}]) |
| $last | 根据资源文档的排序获取最后一个文档数据 | db.mycol.aggregate([{group : {_id : "by_user", last_url : {url"}}}]) |
| $project | 管道操作符 | db.students.aggregate([{ "project": { "学生名称": "name", "age": 1 }}]); |
| $lookup | 关联查询(多张表) | db.customer.aggregate([ {$lookup: { from: "order", localField: "customerCode", foreignField: "customerCode", as: "customerOrder" } } ]).pretty() |
| $unwind | 拆开数组到每一条数据上 | db.group.aggregate([{match: {'url_id': '280793330'}}, {"unwind": "$comments"}]); |
| $addFields | 添加字段 |
# 返回数组最长的两项
# Adds new fields to documents.
# $addFields outputs documents that contain all existing fields from the input documents and newly added fields.
db.group.aggregate([
{ $addFields: { comments: { "$size": { "$ifNull": [ "$comments", [] ] } } } },
{ $sort: { comments: -1 } },
{ $limit: 2}
]);
# 等价于, 这两个添加字段的操作符是等价的
db.group.aggregate([
{ $set: { comments: { "$size": { "$ifNull": [ "$comments", [] ] } } } },
{ $sort: { comments: -1 } },
{ $limit: 2}
]);
# 验证结果的准确
db.group.aggregate([ { "$project" : { "count": { "$size": { "$ifNull": [ "$comments", [] ] } } } } ]).sort({'count': -1});
# 等价于
db.group.aggregate([
{ "$project" : { "count": { "$size": { "$ifNull": [ "$comments", [] ] } } } },
{ $sort: { "count": -1 } },
{ $limit: 2}
]);
db.test_a.insertMany([
{ "_id" : ObjectId("512bc95fe835e68f199c8686"), "author" : "dave", "score" : 80, "views" : 100 },
{ "_id" : ObjectId("512bc962e835e68f199c8687"), "author" : "dave", "score" : 85, "views" : 521 },
{ "_id" : ObjectId("55f5a192d4bede9ac365b257"), "author" : "ahn", "score" : 60, "views" : 1000 },
{ "_id" : ObjectId("55f5a192d4bede9ac365b258"), "author" : "li", "score" : 55, "views" : 5000 },
{ "_id" : ObjectId("55f5a1d3d4bede9ac365b259"), "author" : "annT", "score" : 60, "views" : 50 },
{ "_id" : ObjectId("55f5a1d3d4bede9ac365b25a"), "author" : "li", "score" : 94, "views" : 999 },
{ "_id" : ObjectId("55f5a1d3d4bede9ac365b25b"), "author" : "ty", "score" : 95, "views" : 1000 }
]);
# 先匹配score在70-90之间的, 亦或者views大于等于1000的
# group分组
db.test_a.aggregate( [
{ $match: { $or: [ { score: { $gt: 70, $lt: 90 } }, { views: { $gte: 1000 } } ] } },
{ $group: { _id: null, count: { $sum: 1 } } }
] );
group搭配的操作符
The
<accumulator>operator must be one of the following accumulator operators:
group和distinct一个限制不能返回超过16M的数据
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
$accumulator |
Returns the result of a user-defined accumulator function. |
$addToSet |
Returns an array of unique expression values for each group. Order of the array elements is undefined.Changed in version 5.0: Available in $setWindowFields stage. |
$avg |
Returns an average of numerical values. Ignores non-numeric values.Changed in version 5.0: Available in $setWindowFields stage. |
$bottom |
Returns the bottom element within a group according to the specified sort order.New in version 5.2.Available in $group and $setWindowFields stages. |
$bottomN |
Returns an aggregation of the bottom n fields within a group, according to the specified sort order.New in version 5.2.Available in $group and $setWindowFields stages. |
$count |
Returns the number of documents in a group.Distinct from the $count pipeline stage.New in version 5.0: Available in $group and $setWindowFields stages. |
$first |
Returns a value from the first document for each group. Order is only defined if the documents are sorted.Distinct from the $first array operator.Changed in version 5.0: Available in $setWindowFields stage. |
$firstN |
Returns an aggregation of the first n elements within a group. Only meaningful when documents are in a defined order. Distinct from the $firstN array operator.New in version 5.2: Available in $group, expression and $setWindowFields stages. |
$last |
Returns a value from the last document for each group. Order is only defined if the documents are sorted.Distinct from the $last array operator.Changed in version 5.0: Available in $setWindowFields stage. |
$lastN |
Returns an aggregation of the last n elements within a group. Only meaningful when documents are in a defined order. Distinct from the $lastN array operator.New in version 5.2: Available in $group, expression and $setWindowFields stages. |
$max |
Returns the highest expression value for each group.Changed in version 5.0: Available in $setWindowFields stage. |
$maxN |
Returns an aggregation of the n maximum valued elements in a group. Distinct from the $maxN array operator.New in version 5.2.Available in $group, $setWindowFields and as an expression. |
$mergeObjects |
Returns a document created by combining the input documents for each group. |
$min |
Returns the lowest expression value for each group.Changed in version 5.0: Available in $setWindowFields stage. |
$push |
Returns an array of expression values for documents in each group.Changed in version 5.0: Available in $setWindowFields stage. |
$stdDevPop |
Returns the population standard deviation of the input values.Changed in version 5.0: Available in $setWindowFields stage. |
$stdDevSamp |
Returns the sample standard deviation of the input values.Changed in version 5.0: Available in $setWindowFields stage. |
$sum |
Returns a sum of numerical values. Ignores non-numeric values.Changed in version 5.0: Available in $setWindowFields stage. |
$top |
Returns the top element within a group according to the specified sort order.New in version 5.2.Available in $group and $setWindowFields stages. |
$topN |
Returns an aggregation of the top n fields within a group, according to the specified sort order.New in version 5.2.Available in $group and $setWindowFields stages. |
# 统计某个id出现的次数
db.group.aggregate({
$group: {
_id: "$author_id",
count: {$sum: 1}
}
});
# 出现次数最多的项
db.group.aggregate([
{$group: {_id: "$author_id", count: {$sum: 1}}},
{$sort: {count: -1}},
{$limit: 2}
]);
# 统计嵌套内容中某个项出现的次数
db.group.aggregate([
{$unwind : "$comments"},
{$group : { _id: "$comments.author_id", count: {$sum : 1}}},
{$sort : {count: -1}},
{$limit: 1}
]);
# 取出嵌套内容中的某个项对应的全部内容
db.group.aggregate([
{$unwind : "$comments"},
{$match: {'comments.author_id': '160661798'}},
{$project: {'comments.comment': 1, _id: 0, title: 1}}
]);
六. 备份和恢复
mongorestore版本要和mongodump版本一致
mongodump --version
mongorestore --version
不管是文件的备份还是恢复, 均支持压缩的形式.
# 备份数据, 数据以bson文件存储
mongodump -h dbhost -d dbname -o dbdirectory
mongodump -h localhost -d test_db -o 'C:\Users\Lian\Desktop\test_dump'
# 对文件进行压缩备份
mongodump -h localhost -d test_db -o "C:\Users\Lian\Desktop\test_dump" --gzip
# 恢复数据
mongorestore -h localhost "C:\Users\Lian\Desktop\test_dump"
七. pymongo
注意: client = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017/"), 假如MongoDB service没有启动, 这一步并没有触发Exception.
import pymongo
client = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017/")
# 等价于
client = pymongo.MongoClient(host="localhost",port=27017)
# client类似于mysql, connection
# 获取需要使用的database
db = client['db_name']
# client.database
# 访问集合
collection = db['collection_name']
# db.colllection
# 具体的操作
# 类似于mysql, cursor
cursor = collection.find(query_string)
# 聚合操作
'''
cl.aggregate(
pipeline: Sequence[Mapping[str, Any]],
session: Optional[ForwardRef('ClientSession')] = None,
let: Optional[Mapping[str, Any]] = None,
comment: Optional[Any] = None,
**kwargs: Any,
) -> pymongo.command_cursor.CommandCursor[~_DocumentType]
'''
data = cl.aggregate([{ "$skip": 2 }]);
data
# <pymongo.command_cursor.CommandCursor at 0x1cd7e2d43d0>
pipe = [
{'$unwind' : "$comments"},
{'$group' : { '_id': "$comments.author_id", 'count': {'$sum' : 1}}},
{'$sort' : {'count': -1}},
{'$limit': 1}
]
data = cl.aggregate(pipeline=pipe)
cl.estimated_document_count()
# 返回文档的数量
# 注意排序的参数, 并不是{}
# 顺序参数
# 两个常量
# pymongo.DESCENDING, -1
# pymongo.ASCENDING, 1
data = cl.find().sort('price', -1)
# 关闭退出
client.close()
